Single Layer Materials: A Research On 2D Materials
To understand material systems is the foundation of technology. Depending on the application, materials are specifically chosen that best fits the application intended for example in the construction of buildings, concrete possessing compressive strength makes it an ideal material for the application of building skyscrapers and other buildings.
Understanding the properties of materials is a crucial aspect in proper utilization of materials. In this regard one such feature in fully understanding the behavior of materials is its size, and this is truer when the materials in question are in nanoscale.
Nano materials: An introduction to 2d materials
Nano materials can be broadly classified into; 0D (zero dimensionals), 1D (nanotube/nanowire), 2D (two dimensional) and finally non nano materials also known as bulk materials.
2D materials are materials that only have one dimension nano sized like paper. Made of Crystalline with a single layer of atoms, two dimension materials are also referred to as single layer materials. These are categorized into either 2D allotropes consisting of various elements or compounds which are allotropes with two or more than two covalently bonding elements.
The first modern 2d material, graphene was isolated in 2004, now with research on 2d materials there are several 2d materials in the world.
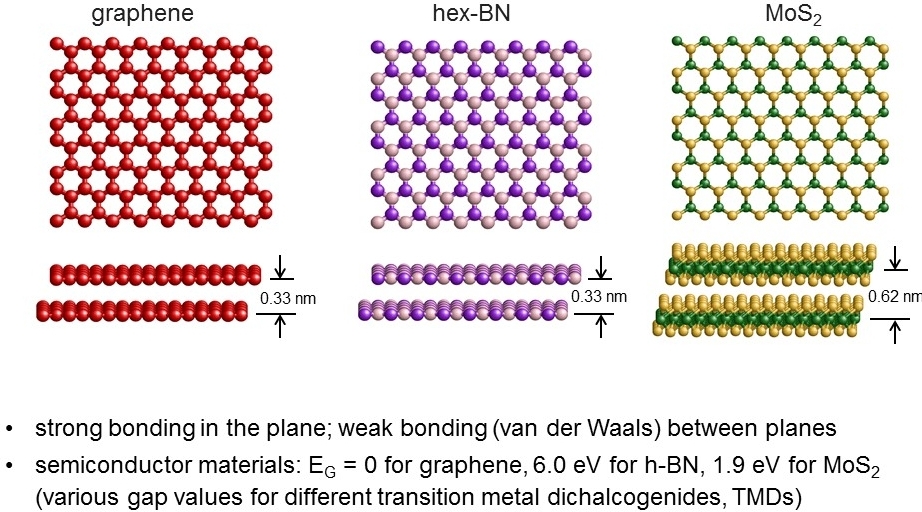
Examples of 2D materials
The first 2d material researched graphene is a lot stronger than steel by its weight and is known for its high conductivity with thermal and electricity
Graphyne structurally similar to graphene is a 2 dimensional allotrope of carbon.
Phosphorene is a two dimensional material made of black phosphorene in a single layer
Xenes is a collective of monolayers that consists of tin (stanene), germanium (germanene) and silicon (silicene). Similar with graphene due to its hexagonal structure but warped to different levels.